Operators in Java
Operators in Java are special symbols that perform operations on operands (variables, values, or expressions) and return a result.
Expression
-
An expression is anything which evaluates to something.
-
Expressions are combinations of operators and operands.
Operator
Operators are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands, and then return a result.
-
Unary : Operates on one operand.
-
Binary : Operates on two operands.
-
Ternary : Operates on three operands.
Types of Operators in Java
| Operator Type | Symbols | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic | +, −, *, /, % | Used for basic mathematical operations. |
| Assignment | =, +=, −=, *=, /=, %= | Assign values to variables, possibly with operations. |
| Increment / Decrement | ++, -- | Increase or decrease a value by 1. |
| Relational | >, <, >=, <=, !=, == | Compare two values; result is boolean (true/false). |
| Logical | &&, ||, ! | Used for logical operations (AND, OR, NOT). |
| Bitwise | &, |, ^, ~ | Perform operations at the bit level. |
| Conditional (Ternary) | ? : | Shortcut for if-else decision making. |
| Shift | <<, >>, >>> | Shift bits left or right. |
| instanceof | instanceof | Tests whether an object is an instance of a class. |
1. Arithmetic Operator
Arithmetic operators in Java are used to perform basic mathematical calculations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus.
| Operator | Example |
|---|---|
| + (Addition) | 4 + x + 5 + y |
| − (Subtraction) | 4 - x - 5 - y |
| * (Multiplication) | 4 * x * 5 |
| / (Division) | 50 / x |
| % (Modulus) | 9 % 4 → 1 |
Compound Expression Examples:
3 * x + 5 - 7
principle + (principle + interest)
2. Assignment Operator
- The assignment operator has the lowest precedence of all operators.
- It is always evaluated last.
- It assigns the value of an expression to a variable.
- The previous value of the variable is overwritten by the new expression value.
Syntax: variable = expression
Examples:
x = x + 10;
isVisible = true;
timeInSecond = distance / speedOfLight;
Code Example:
// Add Assignment (+=) int a = 20; a += 5; // same as a = a + 5; System.out.print(a); // OUTPUT: 25 // Multiply Assignment (*=) a *= 5; // same as a = a * 5; System.out.print(a); // OUTPUT: 100 // Other compound assignments: // -=, /=, %=, <<=, >>=, &=, ^=, |=
3. Increment / Decrement Operator
These operators are used to increase or decrease the value of a variable by 1.
++
--
Code Example:
int x = 5; System.out.println(++x); // OUTPUT: 6 (pre-increment) System.out.println(x++); // OUTPUT: 6 (post-increment, x=7 afterwards) System.out.println(--x); // OUTPUT: 6 (pre-decrement) System.out.println(x--); // OUTPUT: 6 (post-decrement, x=5 afterwards)
4. Relational Operator
Relational operators are used to compare two values.
The result of a relational expression is always a boolean → true or false.
| Operator | Description | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
> |
Greater Than | (5 > 10) |
false |
< |
Less Than | (5 < 10) |
true |
== |
Equal To | (5 == 5) |
true |
!= |
Not Equal To | (5 != 2) |
true |
>= |
Greater Than or Equal To | (10 >= 5) |
true |
<= |
Less Than or Equal To | (10 <= 5) |
false |
Code Example:
int a = 5, b = 10; System.out.println(a > b); // false System.out.println(a < b); // true System.out.println(a == b); // false System.out.println(a != b); // true a = 10; b = 5; System.out.println(a >= b); // true System.out.println(a <= b); // false
5. Logical Operator
Logical operators are used when we want to combine multiple relational expressions.
The result of a logical expression is always a boolean (true or false).
Logical AND (&&)
Returns true only if both expressions are true.
| Exp1 | Exp2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| true | true | true |
| true | false | false |
| false | true | false |
| false | false | false |
Logical OR (||)
Returns true if at least one expression is true.
| Exp1 | Exp2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| true | true | true |
| true | false | true |
| false | true | true |
| false | false | false |
Logical NOT (!)
Flips the result: true → false, false → true.
| Expr | Result |
|---|---|
| true | false |
| false | true |
Code Example
int x = 6;
boolean b1 = (x > 5) && (x < 10);
System.out.println(b1); // true
boolean b2 = (x > 5) && (x != 6);
System.out.println(b2); // false
boolean b3 = (x > 5) || (x != 6);
System.out.println(b3); // true
boolean b4 = !(x > 5);
System.out.println(b4); // false
6. Bitwise Operator
Bitwise operators perform operations directly on the bits of numbers.
| A | B | A & B | A | B | A ^ B | ~A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Code Example
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 6; // 0000 0110
int b = 3; // 0000 0011
int r1 = a & b; // 2
int r2 = a | b; // 7
int r3 = a ^ b; // 5
int r4 = ~a; // -7
System.out.println(r1 + ", " + r2 + ", " + r3 + ", " + r4);
}
}
Explanation:
a = 6 (0000 0110), b = 3 (0000 0011)
a & b = 2, a | b = 7, a ^ b = 5, ~a = -7
7. Conditional Operator (? :)
Conditional (ternary) operator is a shorthand if-else that evaluates a boolean expression and returns one of two values.
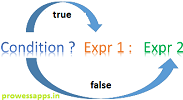
Code Example
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10, b = 20;
int max = (a > b) ? a : b;
System.out.println("Max = " + max);
}
}
Output: Max = 20
8. Shift Operator ( << ,>> , >>> )
Shift operators are used to move the bits of a number towards left or right. They are commonly used for fast multiplication/division by powers of 2.
- Left Shift ( << ): Shifts bits to the left, filling with 0s. Equivalent to multiplying by 2 for each shift.
- Right Shift ( >> ): Shifts bits to the right, preserving the sign bit (MSB).
- Unsigned Right Shift ( >>> ): Shifts bits to the right, filling with 0s (ignores sign bit).
Code Example
// 1. Left Shift ( << )
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 6 << 2;
System.out.println(x);
// OUTPUT: 24
}
}
// 2. Right Shift ( >> )
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 6 >> 2;
System.out.println(x);
// OUTPUT: 1
}
}
// 3. Unsigned Right Shift ( >>> )
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 6 >>> 2;
System.out.println(x);
// OUTPUT: 1
}
}
Explanation
6 << 2
6 = 0000 0110
1st shift -> 0000 1100
2nd shift -> 0001 1000 = 24
6 >> 2
6 = 0000 0110
1st shift -> 0000 0011
2nd shift -> 0000 0001 = 1
9. instanceof Operator
The instanceof operator is used only for object reference variables.
It checks whether an object is an instance of a particular class or implements an interface.
The result is always a boolean value (true or false).
Syntax
(ref.variable) instanceof (class/interface)
Code Example
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Ayan";
// returns true since 'name' is of type String
boolean res = name instanceof String;
System.out.println(res);
}
}
Output: true
Operator Precedence
When more than one operator is used in an expression, Java follows a predefined rule of priority that decides which operator is evaluated first. This rule is known as operator precedence.
Note: If two operators have the same precedence, the expression is evaluated based on their associativity.
Most operators are left-to-right, but assignment (=, +=, -=, etc.) is right-to-left.
Java Operator Precedence Table
| Precedence | Operator | Description | Associativity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | () , [] , . | Parentheses, Array, Member Access | Left-to-Right |
| 2 | ++ , -- , + (unary), - (unary), ! , ~ | Unary operators | Right-to-Left |
| 3 | * , / , % | Multiplication, Division, Modulus | Left-to-Right |
| 4 | + , - | Addition, Subtraction | Left-to-Right |
| 5 | << , >> , >>> | Shift operators | Left-to-Right |
| 6 | < , <= , > , >= , instanceof | Relational operators | Left-to-Right |
| 7 | == , != | Equality operators | Left-to-Right |
| 8 | & | Bitwise AND | Left-to-Right |
| 9 | ^ | Bitwise XOR | Left-to-Right |
| 10 | | | Bitwise OR | Left-to-Right |
| 11 | && | Logical AND | Left-to-Right |
| 12 | || | Logical OR | Left-to-Right |
| 13 | ? : | Ternary Conditional | Right-to-Left |
| 14 | = , += , -= , *= , /= , %= , &= , ^= , |= , <<= , >>= , >>>= | Assignment operators | Right-to-Left |
Source: prowessapps.com
🚀 Quick Knowledge Check
Topic: Operators | Language: Java
Q1. Which operator is known as the ternary operator in Java?
Q2. What will be the output of this code?
int x = 5;
System.out.println(x++ + ++x);Q3. What is the result of 10 >> 2?
System.out.println(10 >> 2);Q4. Which operator is used for short-circuit AND?
Q5. What will be the output of this code?
int a = 5, b = 10;
System.out.println(a > b ? a : b);Q6. Which of the following is a bitwise AND operator in Java?
Q7. Which operator has the highest precedence in Java?
Q8. Which operator is used to check object type?
String name = "Ayan";
boolean res = name instanceof String;
System.out.println(res);Q9. The associativity of the assignment operator (=) in Java is:
Q10. What will be the output of this code?
System.out.println(10 % 3);