Compile and Run First Java Program
In this section we will learn how to write and execute a simple Java program.
-
To write a Java program you can use any text editor like Notepad, Notepad++ (Windows) or gedit (Linux).
-
You can also use popular IDEs such as BlueJ, NetBeans, or Eclipse to write and execute Java programs.
-
To compile your Java source code, you need a Java Compiler, and to run it, you need a Java Interpreter. Both are included in the JDK. Ensure JDK is installed and configured in your system.
Steps in Programming with Java
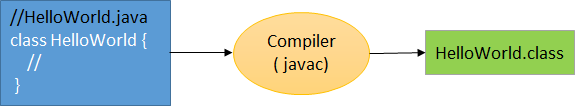
1. Create the Source Code
Write your program using a text editor and save it with the extension .java.
Example: HelloWorld.java
2. Compile the Program
Use the command:
javac HelloWorld.java
After successful compilation, a HelloWorld.class file (bytecode) will be generated.
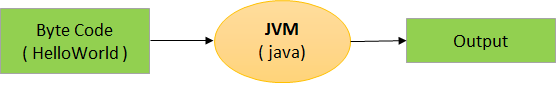
3. Execute the Program
Run the program using:
java HelloWorld
Note: Do not include .class in the execution command.
Example: HelloWorld.java
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
} 
Explanation
- class: keyword to declare a class.
- public: access specifier, visible to all.
- static: method belongs to class, no object needed.
- void: return type, means no value returned.
- main: entry point of the program.
- String[] args: stores command-line arguments.
- System.out.println(): outputs text to console.
Source Code Facts
- Written by programmer in high-level language.
- Saved with
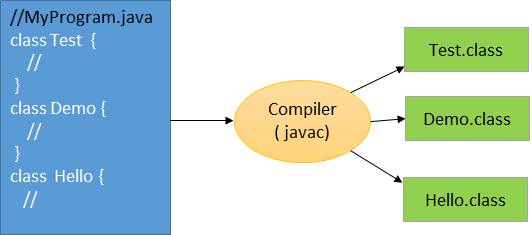
.javaextension. - May contain multiple classes, but only one public class.
- If a public class exists, filename must match the class name.
- Structure:
package declaration; import statements; class ClassName { // class members }
Bytecode Facts
- Compiler generates bytecode (.class file).
- Bytecode is intermediate and platform-independent.
- Only JVM can interpret and run bytecode.
- Each class generates its own bytecode file.
- Example:
HelloWorld.class - If a class is run directly by JVM, it must contain the main() method.
🚀 Quick Knowledge Check
Topic: Writing_executing_java | Language: Java